One of the most common company comparisons of the past few years that I’ve stumbled upon is between Intel Corporation (NASDAQ:INTC) and Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (NYSE:AMD) – two of the leaders in the computer chip industry. Of course, Intel Corporation (NASDAQ:INTC) is ahead of Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (NYSE:AMD) in the race. However, with lots of information out on the table about these two companies, how do their valuations compare?
While there are hundreds of things to consider when deciding whether one or the other belongs in your portfolio, one helping hand can be potential over- or undervaluation of either company. Here, I am going to use three different methods of valuating companies to show which takes the over/undervaluation title home, and to hopefully introduce you to a few handy metrics.
PEG Ratio
The PEG ratio (the Price/Earnings to Growth Ratio) helps to show the relationship between the price of a stock, the earnings per share, and the growth rate of the company. This metric is particularly useful when comparing companies side by side with different PE ratios and different growth rates. When analyzing the ratio, analysts typically classify companies with a PEG lower than 1 as associated with undervaluation, while companies above 1 tend to be overvalued. Now, let’s take a look at the graph for these two chip makers:
Clearly, Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (NYSE:AMD) is potentially way overvalued, while Intel Corporation (NASDAQ:INTC) is potentially undervalued. This makes sense when looking at it from another angle; say, the value score angle. The value score is a measure from 1-10, from companies with a 10 tend to substantially outperform the S&P 500 and companies with a 1 tend to do the opposite. Intel’s score of 10 with their stock price (at time of writing, about $28.11) seem to add up to a summary of undervaluation. AMD’s value score over the last few years has been mostly about 4, with rare appearances around 6. So, according to this metric, Intel Corporation (NASDAQ:INTC) is potentially undervalued while Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (NYSE:AMD) is potentially overvalued. Let’s move on to the next one.
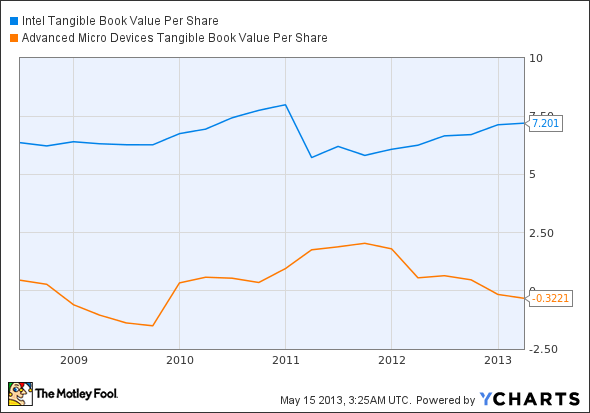
Tangible Book Value Per Share
Tangible book value per share, or TBVPS, is a measurement of the portion of tangible assets (all assets, with the exception of goodwill and items classified as “intangible” on a company’s balance sheet) attributable to each share of the company’s common stock. What this means is that it is helpful in establishing the valuation of a company, and whether it may be over or undervalued. This is important because lots of companies’ balance sheets can reflect asset valuations that are inflated by intangibles; yet, if a company were to go bankrupt, the tangible value of assets a company has would be what is left over after bankruptcy. A simple way to put this would be that tangible book value answers the question, “as a shareholder, what would I receive if the company had to liquidate all of its assets?” By measuring this value per share, we create a ratio that measures valuation.
A TBVPS larger than the current price of the stock means that the stock could be potentially overvalued, whereas, obviously, a TBVPS smaller than the stock could mean that the stock is potentially undervalued. The formula, for those who are interested, for TBVPS is equal to: (Tangible Book Value – Book Value of Preferred Stock) / Common Shares Outstanding. Now, let’s look at each company’s TBVPS in relation to their stock price.
| TBVPS | Price ($) | TBVPS / Price (Valuation) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intel | 7.20 | 28.11 | .26 |
| AMD | -0.32 | 8.02 | -.04 |
So, according to this metric, both companies are potentially undervalued, with both companies having a TBVPS / Price ratio substantially below 1. Let’s move on to the third metric.