Introduction
Gas fees are an unavoidable cost in cryptocurrency, affecting everything from trading and investing to gaming, DeFi, and NFT transactions. Traders frequently encounter gas fees when moving assets across exchanges, while investors and gamblers must compare cryptocurrencies for gambling and navigate fluctuating transaction costs for staking, gaming, and smart contract interactions.
This article breaks down gas fees across crypto trading, gambling, NFTs, and DeFi, helping traders and investors optimize costs and choose the most efficient networks.
It also analyzes which blockchains and cryptocurrencies offer the lowest fees and how Layer 2 solutions are making transactions faster and cheaper.
What Are Gas Fees, and Why Do They Matter?
Gas fees are transaction costs paid to blockchain validators for processing transactions. These fees depend on:
- Network congestion – The busier the network, the higher the fees.
- Transaction complexity – Simple transfers cost less, while smart contract interactions require more processing power.
- Blockchain type – Ethereum fees are typically higher than Solana or BNB Chain due to its decentralized structure.
For traders, gas fees directly impact profitability, especially for high-frequency trading or arbitrage. Investors in NFTs and DeFi are also not protected.
On the other hand, those who play with Solana pay minimal transaction costs, which preserves more of their bankroll for actual gameplay instead of network fees—which may not be the case if transactions were made in ETH, for example.
Gas Fees in Crypto Trading
For active traders, gas fees can significantly affect profitability, especially in high-frequency trading (HFT) or arbitrage strategies. On-chain traders often factor in gas costs when deciding between short-term trades or holding positions—for example, Ethereum-based DEX users may lose potential gains if gas fees exceed trading profits, making Solana, BNB Chain, or Layer 2 networks more attractive for low-cost trading. Additionally, automated trading bots operating on Ethereum Layer 1 require careful fee optimization to remain profitable, while lower-cost networks enable more efficient algorithmic strategies.
Where Traders Pay Gas Fees
Gas fees in trading depend on whether users trade on centralized exchanges (CEXs) or decentralized exchanges DEXs.
- CEX Trading (Binance, Coinbase, Kraken)
- No gas fees for on-platform trades (trades occur off-chain).
- Fees apply when depositing or withdrawing crypto (exchange-set fees).
- DEX Trading (Uniswap, PancakeSwap, dYdX)
- Trades execute on-chain, meaning gas fees apply for every order and swap.
- Fees depend on blockchain congestion—Ethereum swaps can cost $1–$3 during low traffic, but can surpass $50+ during peak congestion.
- Layer 2 solutions (Optimism, Arbitrum) help cut gas fees by bundling transactions, reducing costs by 3–100× compared to Ethereum’s main network.
DEX vs. CEX Fee Comparison
| Transaction Type | Centralized Exchange (CEX) | Decentralized Exchange (DEX) |
| Trading Fee | 0.1% (Binance) – 0.5% (Coinbase) | Network gas fee (~$0.03 on BNB Chain, ~$3 on Ethereum) |
| Deposit Fee | Free or low (~$0.50–$10) | Gas fee (~$0.05 on BNB, ~$15 on Ethereum) |
| Withdrawal Fee | Exchange-set fee (~$0.10–$25) | Gas fee (~$0.01–$50 based on network) |
Many traders prefer Layer 2 solutions or low-fee chains like Solana or BNB Chain for cost efficiency.
Gas Fees in Crypto Gambling
Crypto gambling platforms process deposits, withdrawals, and in-game betting transactions using blockchain networks. The cost and speed of these transactions depend on whether they occur on-chain, off-chain, or via Layer 2 solutions.
Choosing the right cryptocurrency can make a significant difference in transaction costs, and you can easily compare cryptocurrencies for gambling to find the most cost-effective options.
Comparison of Gambling Transaction Methods
| Transaction Type | Speed | Security | Transparency | Use Case |
| On-Chain | Moderate-Slow | High | Complete | High-value transactions requiring maximum security |
| Layer 2 On-Chain | Fast | High | High | Balance of security and speed |
| Off-Chain/Custodial | Instant | Moderate | Limited | Micro-transactions, rapid gameplay |
Casinos favor BNB Chain, Solana, and Layer 2 solutions for their low fees and high-speed transactions.
Gas Fees in NFT Transactions
NFT transactions incur gas fees for minting, buying, selling, and transferring assets. Ethereum-based NFTs are the most expensive, whereas Layer 2 networks and alternative chains offer lower costs.
| Transaction Type | Ethereum | Polygon (L2) | Solana |
| Minting an NFT | $10–$50 | ~$0.05 | ~$0.005 |
| Buying/Selling | $5–$20 | ~$0.01 | ~$0.005 |
| Transferring | ~$2–$10 | ~$0.001 | ~$0.002 |
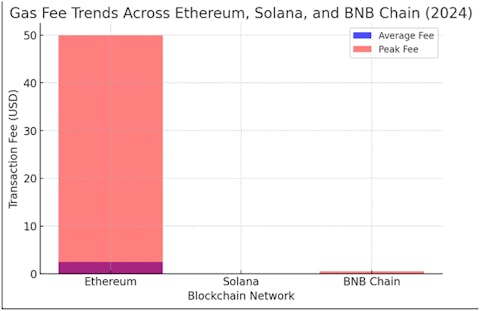
Gas Fee Trends Across Major Blockchains
The cost of transactions varies widely across blockchain networks. Ethereum remains the most expensive, while Solana and BNB Chain offer the lowest fees. The chart below visualizes the differences.
Gas Fee Trends: Ethereum vs. Solana vs. BNB Chain
How to Minimize Gas Fees for Trading, Gambling, and DeFi
- Use Layer 2 Solutions – Rollups like Arbitrum & Optimism can reduce Ethereum gas fees by 3–100×.
- Choose Low-Fee Blockchains – BNB Chain and Solana offer the best speed-to-cost balance.
- Time Transactions Wisely – Gas fees fluctuate; use fee trackers to optimize timing.
- Batch Transactions – Combining multiple actions into a single transaction reduces costs.
- Consider Off-Chain or Hybrid Solutions – Off-chain casinos provide instant transactions with no gas fees.
Best Cryptocurrencies for Low-Fee Transactions
Some cryptocurrencies are better suited for low-cost transactions, depending on the use case:
| Cryptocurrency | Use Case | Average Fee | Best Feature |
| USDT, USDC, DAI (Stablecoins) | Payments & Trading | Varies (depends on chain) | Cheapest on Solana & BNB Chain |
| Bitcoin (BTC) w/ Lightning Network | Fast P2P Payments | < $0.01 | Instant BTC transactions |
| Solana (SOL) | Trading & Gambling | ~$0.005 | High-speed, low-fee transactions |
| BNB (BNB Chain) | DeFi & Exchanges | ~$0.10 | Cheap for trading & gaming |
| Polygon (MATIC) | DeFi & NFTs | ~$0.01 | Ethereum compatibility with low fees |
- Best for Traders? BNB Chain & Solana
- Best for Gamblers? Solana & Layer 2 Blockchains
- Best for DeFi? Ethereum Layer 2 & BNB Chain
Conclusion
Gas fees impact traders, investors, and crypto gamblers, but choosing the right network can drastically reduce transaction costs.
- Traders should favor Solana, BNB Chain, or Ethereum Layer 2s.
- Gamblers benefit from Layer 2 or off-chain solutions.
- Ethereum is dominant for DeFi and NFTs, but users should optimize costs with Layer 2 rollups.
For real-time gas fee updates, platforms like Etherscan Gas Tracker, GasNow, and Dune Analytics provide live tracking tools to help optimize your transactions.





